This architectural style, developed over centuries, reflects the unique aesthetics and philosophy of Japanese life, where beauty lies in simplicity and functionality.
Traditional Japanese houses, known as minka, are perfect examples of this approach. Built primarily from wood, these residences feature thatched or clay tile roofs and flexible interiors divided by sliding paper (shoji) doors and tatami floors. The use of natural materials and harmonious integration with the surroundings reflect the Japanese belief that buildings should coexist in balance with nature.
Japanese castles, or shiro, are impressive structures that combine fortification and elegance. Notable examples include Himeji Castle, with its white walls and curved roofs, which resemble a heron in flight. These castles not only served as residences for feudal lords, but also as centers of administration and defense, designed to withstand attacks and sieges.
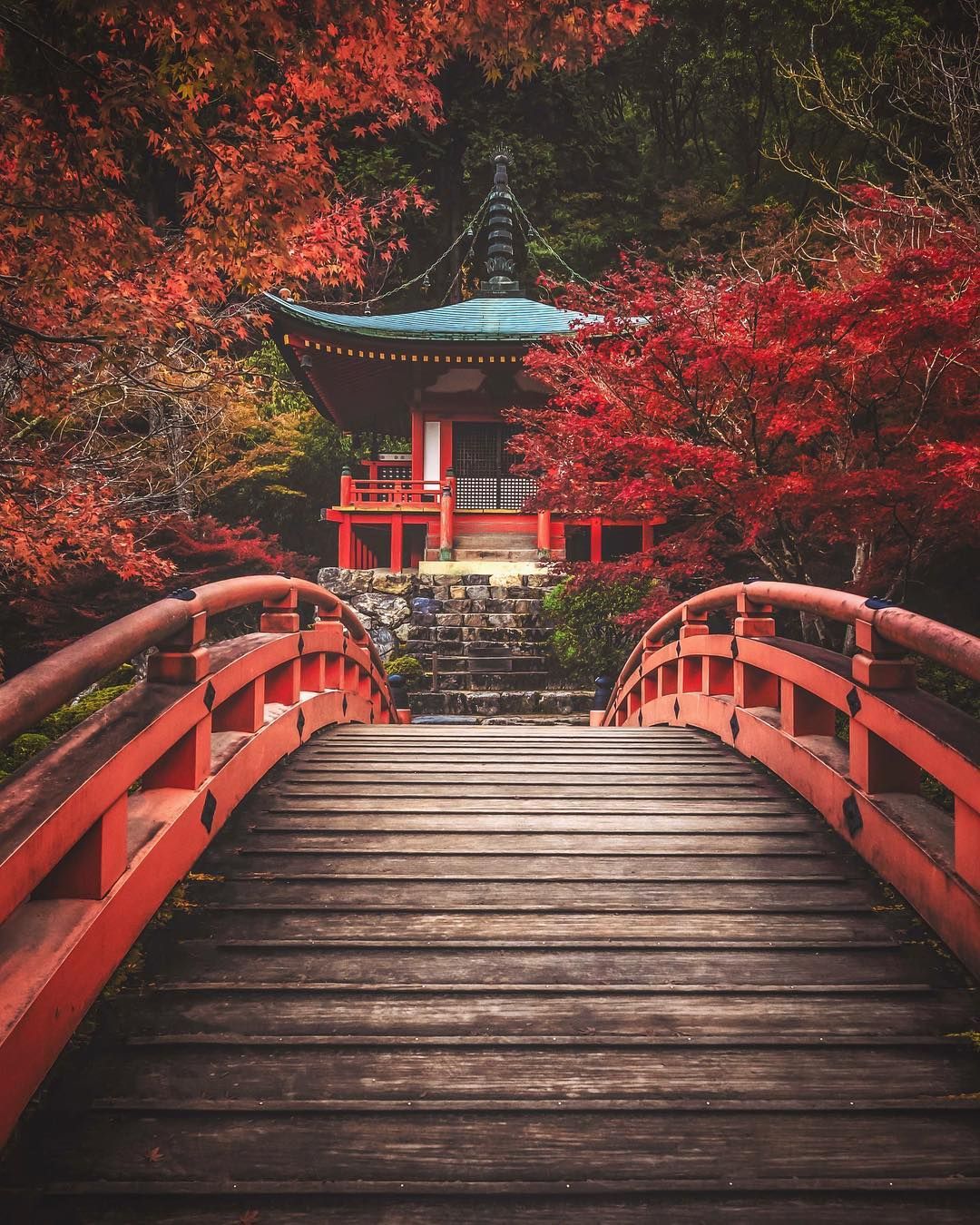
Japan's religious architecture, exemplified by Buddhist temples and Shinto shrines, is equally notable. Temples, such as Kinkaku-ji Temple in Kyoto, with its golden pavilion shining over a serene lake, and Senso-ji Temple in Tokyo, one of the oldest and most revered in the country, are built with precision craftsmanship and adorned with rich detail. . Shinto shrines, such as Ise Shrine, are known for their purity and simplicity, often constructed of unpainted wood to reflect the aesthetics of the natural.
Another important aspect of traditional Japanese architecture is the garden, which is considered an extension of the living space. Zen gardens, such as the famous Ryoan-ji Garden, use carefully arranged rocks, sand and vegetation to create miniature landscapes that invite meditation and contemplation. These gardens are designed to evoke natural beauty in a controlled, organized space.